Resize images on upload to S3 using Lambda and .NET
Imagine you’re making a website on AWS where users can upload pictures (whether avatars, profile covers, or photos of kittens). These pictures need to show up in different sizes, like small thumbnails or big versions. But if users have to download the full-size images every time, it’ll slow down the site, especially for those with poor connection. Slow site means loss of users, sales and even search engines rankings. Let’s keep it fast and make the images load faster. There are at least two options:
- compress the images to all necessary sizes upon uploading to the site:
- compress the corresponding image to the appropriate size before sending it to the user.
In this article, we’ll focus on the first option.
Architecture
We will implement a public API using API Gateway and Lambda to upload images, which we will store in an S3 bucket. Upon each file upload to the images/ folder in S3, another Lambda function will be triggered, responsible for creating all necessary image versions and placing them in the resized/ folder. This will allow us to separate originals from processed versions. All images will be accessible via public URLs generated by S3.
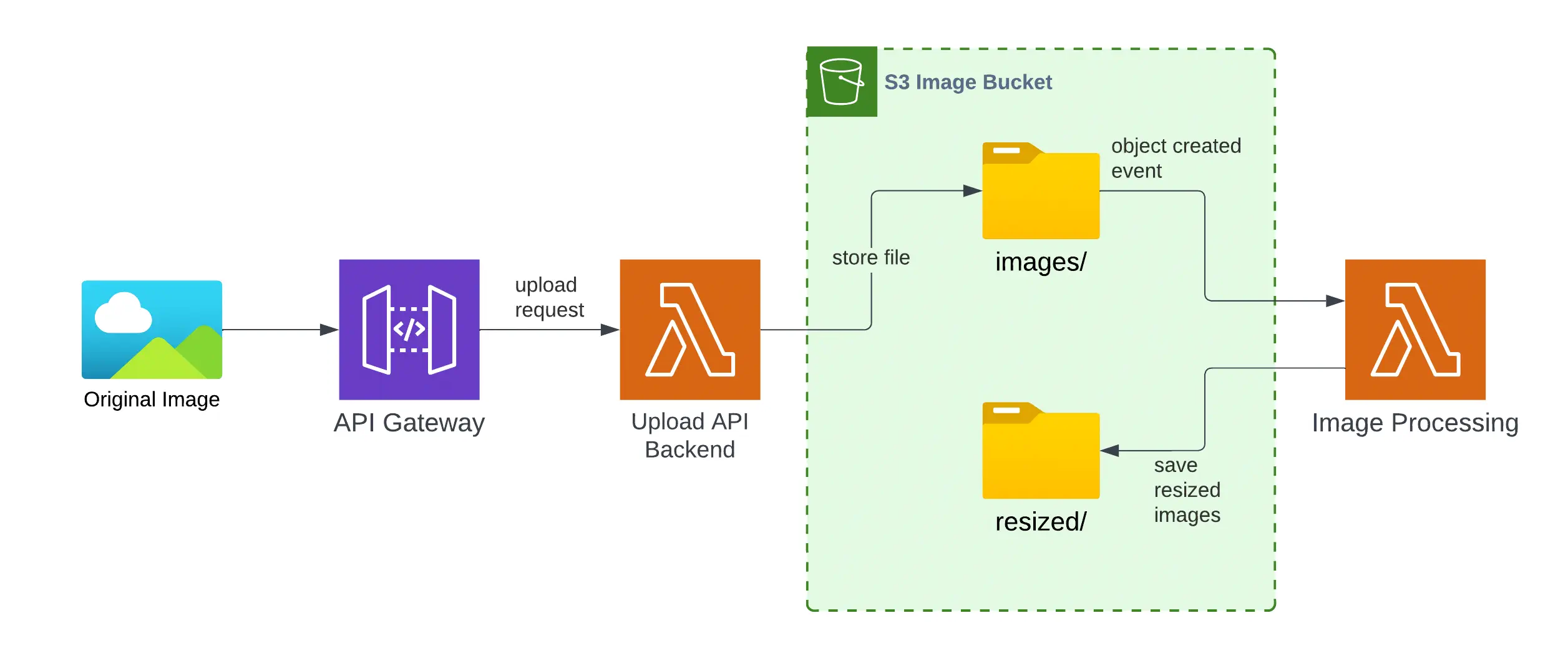
Implementation
Image Processing Lambda
Let’s start with the most crucial part, which is image processing. For this, we’ll utilize the SkiaSharp library, which is a wrapper for Skia from Google. It’s fast and cross-platform, allowing us to use it in AWS Lambda.
To begin, let’s add the necessary packages to our project. We’ll only need two packages: SkiaSharp and SkiaSharp.NativeAssets.Linux.NoDependencies. The first package contains the library itself, while the second one includes native files for Linux, enabling us to use the library in AWS Lambda.
dotnet add package SkiaSharp
dotnet add package SkiaSharp.NativeAssets.Linux.NoDependenciesThe code of the Lambda function looks like this:
using Amazon.Lambda.Core;
using Amazon.Lambda.S3Events;
using Amazon.S3;
using Amazon.S3.Model;
using SkiaSharp;
using System.Text.Json;
using static Amazon.Lambda.S3Events.S3Event;
// Assembly attribute to enable the Lambda function's JSON input to be converted into a .NET class.
[assembly: LambdaSerializer(typeof(Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson.DefaultLambdaJsonSerializer))]
namespace ImageResizeLambda;
public class Function
{
private readonly IAmazonS3 _s3Client;
// Predefined sizes for images
private readonly List<(int Width, int Height, string Label)> _wideSizes = [(1280, 720, "L"), (1200, 628, "M"), (854, 480, "S"), (427, 240, "XS")];
private readonly List<(int Width, int Height, string Label)> _tallSizes = [(720, 1280, "L"), (628, 1200, "M"), (480, 854, "S"), (240, 427, "XS")];
private readonly List<(int Width, int Height, string Label)> _squareSizes = [(1080, 1080, "SL"), (540, 540, "SM"), (360, 360, "SS"), (180, 180, "SXS")];
private readonly string _resizedObjectPath;
private readonly bool _convertToWebp;
private readonly int _convertQuality;
public Function() : this(new AmazonS3Client())
{
}
public Function(IAmazonS3 s3Client)
{
this._s3Client = s3Client;
_resizedObjectPath = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("RESIZED_OBJECT_PATH") ?? "/resized/";
_convertToWebp = bool.TryParse(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CONVERT_TO_WEBP"), out bool convert) && convert;
_convertQuality = int.TryParse(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CONVERT_QUALITY"), out int quality) ? quality : 100;
}
public async Task FunctionHandler(S3Event evnt, ILambdaContext context)
{
context.Logger.LogLine($"Received S3 event: {JsonSerializer.Serialize(evnt)}");
var eventRecords = evnt.Records ?? new List<S3EventNotificationRecord>();
foreach (var s3EventEntity in eventRecords.Select(r => r.S3))
{
try
{
using var streamResponse = await this._s3Client.GetObjectStreamAsync(s3EventEntity.Bucket.Name, s3EventEntity.Object.Key, null);
using var memoryStream = new MemoryStream();
streamResponse.CopyTo(memoryStream);
memoryStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
using var bitmap = SKBitmap.Decode(memoryStream);
if (bitmap == null)
{
context.Logger.LogError($"Error decoding object {s3EventEntity.Object.Key} from bucket {s3EventEntity.Bucket.Name}.");
continue;
}
var sizes = bitmap.Height > bitmap.Width ? _tallSizes : _wideSizes;
foreach (var size in sizes)
{
await ResizeAndPut(s3EventEntity, bitmap, size.Width, size.Height, size.Label, context.Logger);
}
foreach (var size in _squareSizes)
{
await ResizeAndPut(s3EventEntity, bitmap, size.Width, size.Height, size.Label, context.Logger);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
context.Logger.LogError($"Error getting object {s3EventEntity.Object.Key} from bucket {s3EventEntity.Bucket.Name}.");
context.Logger.LogError(e.Message);
context.Logger.LogError(e.StackTrace);
throw;
}
}
}
private async Task ResizeAndPut(S3Entity s3EventEntity, SKBitmap bitmap, int width, int height, string sizeLabel, ILambdaLogger logger)
{
string filePath = Path.GetDirectoryName(s3EventEntity.Object.Key) ?? string.Empty;
string fileExtension = Path.GetExtension(s3EventEntity.Object.Key);
string filename = Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(s3EventEntity.Object.Key) + (_convertToWebp ? ".webp" : fileExtension);
string destination = Path.Combine(_resizedObjectPath, filePath, sizeLabel, filename);
logger.LogLine($"Resizing {s3EventEntity.Object.Key} to {width}x{height} and putting it to {destination}");
try
{
using var resizedBitmap = bitmap.Resize(new SKImageInfo(width, height), SKFilterQuality.High);
using var image = SKImage.FromBitmap(resizedBitmap);
using var data = image.Encode(GetEncodedImageFormat(_convertToWebp, fileExtension), _convertQuality);
using var ms = new MemoryStream();
data.SaveTo(ms);
ms.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
var request = new PutObjectRequest
{
BucketName = s3EventEntity.Bucket.Name,
Key = destination,
InputStream = ms
};
await this._s3Client.PutObjectAsync(request);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
logger.LogError($"Error processing {s3EventEntity.Object.Key}: Destination: {destination}, Width: {width}, Height: {height}");
logger.LogError(e.Message);
logger.LogError(e.StackTrace);
}
}
// Helper method to get the image format based on the file extension and the convertToWebp flag
private static SKEncodedImageFormat GetEncodedImageFormat(bool convertToWebp, string fileExtension) =>
convertToWebp ? SKEncodedImageFormat.Webp : fileExtension.ToLower() switch
{
".png" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Png,
".jpg" or ".jpeg" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Jpeg,
".gif" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Gif,
".bmp" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Bmp,
".wbmp" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Wbmp,
".dng" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Dng,
".heif" or ".heic" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Heif,
".webp" => SKEncodedImageFormat.Webp,
_ => SKEncodedImageFormat.Png
};
}Our function is configured via the following environment variables:
RESIZED_OBJECT_PATH- the path where processed images will be stored.CONVERT_TO_WEBP- a flag indicating whether to convert images to the (WebP)[https://developers.google.com/speed/webp/] format (a progressive modern format that further accelerates loading).CONVERT_QUALITY- conversion quality from 0 to 100.
API Gateway
To allow users to upload images to our website, we need to create a public API. For the API Gateway backend, we’ll use a Lambda function that will store uploaded files in S3. Let’s start by creating the function based on .NET Minimal API:
DisableAntiforgery to our endpoint to avoid anti-forgery issues. Do not do this in production.
Also, we added UseSwagger and UseSwaggerUI to be able to test our API via Swagger.using Amazon.S3;
using Amazon.S3.Model;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add AWS Lambda support. When application is run in Lambda Kestrel is swapped out as the web server with Amazon.Lambda.AspNetCoreServer. This
// package will act as the webserver translating request and responses between the Lambda event source and ASP.NET Core.
builder.Services.AddAWSLambdaHosting(LambdaEventSource.HttpApi);
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
// Enable middleware to serve generated Swagger as a JSON endpoint.
// Don't do this in production, as it's a security risk.
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
var s3Client = new AmazonS3Client();
var bucketName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("BUCKET_NAME") ?? "fastfoodcoding-imageprocessing";
var uploadPath = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("UPLOAD_PATH") ?? "images/";
var allowedExtensions = new[] { ".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png", ".gif", ".bmp", ".webp", ".dng", ".heif", ".heic", ".wbmp" };
// upload file endpoint (images)
app.MapPost("/upload", async (IFormFile file) =>
{
if (file == null || file.Length == 0)
{
return Results.BadRequest("File is empty");
}
// only allow certain file extensions
if (!allowedExtensions.Contains(Path.GetExtension(file.FileName).ToLower(), StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
return Results.BadRequest("Invalid file extension");
}
// don't allow files larger than 25MB
if (file.Length > 25 * 1024 * 1024)
{
return Results.BadRequest("File is too large");
}
using var inputStream = file.OpenReadStream();
using var memoryStream = new MemoryStream();
inputStream.CopyTo(memoryStream);
memoryStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
var putRequest = new PutObjectRequest
{
BucketName = bucketName,
Key = Path.Combine(uploadPath, file.FileName),
InputStream = memoryStream
};
var response = await s3Client.PutObjectAsync(putRequest);
return Results.StatusCode((int)response.HttpStatusCode);
})
.DisableAntiforgery(); // Disable antiforgery for this endpoint. Don't do this in production.
app.Run();This function is configured via the following environment variables:
BUCKET_NAME- the name of the S3 bucket where uploaded files will be stored.UPLOAD_PATH- the path for storing files.
CDK
To deploy our solution, we will use AWS CDK. Let’s create a Stack that will contain our Lambda functions, S3 bucket, and API Gateway.
using Amazon.CDK;
using Amazon.CDK.AWS.Apigatewayv2;
using Amazon.CDK.AWS.IAM;
using Amazon.CDK.AWS.Lambda;
using Amazon.CDK.AWS.S3;
using Amazon.CDK.AWS.S3.Notifications;
using Amazon.CDK.AwsApigatewayv2Integrations;
using Constructs;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace FastFoodCoding.ImageProcessing.Cdk
{
public class ImageProcessingCdkStack : Stack
{
internal ImageProcessingCdkStack(Construct scope, string id, IStackProps props = null) : base(scope, id, props)
{
var bucketName = new CfnParameter(this, "BucketName", new CfnParameterProps
{
Type = "String",
Description = "The name of the S3 bucket to store images",
Default = "fastfoodcoding-imageprocessing"
});
var sourceFolder = new CfnParameter(this, "SourceFolder", new CfnParameterProps
{
Type = "String",
Description = "The name of the folder in the S3 bucket to store images",
Default = "images"
});
var destinationFolder = new CfnParameter(this, "DestinationFolder", new CfnParameterProps
{
Type = "String",
Description = "The name of the folder in the S3 bucket to store resized images",
Default = "r"
});
// define a public S3 bucket to store images
var s3Bucket = new Bucket(this, "ImageBucket", new BucketProps
{
BucketName = bucketName.ValueAsString,
RemovalPolicy = RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
BlockPublicAccess = new BlockPublicAccess(new BlockPublicAccessOptions
{
BlockPublicAcls = false,
IgnorePublicAcls = false,
BlockPublicPolicy = false,
RestrictPublicBuckets = false
})
});
// allow anyone to read objects from the bucket
s3Bucket.AddToResourcePolicy(new PolicyStatement(new PolicyStatementProps
{
Actions = ["s3:GetObject"],
Resources = [s3Bucket.ArnForObjects("*")],
Principals = [new StarPrincipal()]
}));
// allow the lambda function to read and write objects to the bucket
var imageResizeLambdaRole = new Role(this, "ImageResizeLambdaRole", new RoleProps
{
AssumedBy = new ServicePrincipal("lambda.amazonaws.com"),
ManagedPolicies =
[
ManagedPolicy.FromAwsManagedPolicyName("service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole")
],
InlinePolicies = new Dictionary<string, PolicyDocument>
{
["S3Policy"] = new PolicyDocument(new PolicyDocumentProps
{
Statements =
[
new PolicyStatement(new PolicyStatementProps
{
Actions = ["s3:GetObject", "s3:PutObject"],
Resources = [s3Bucket.ArnForObjects("*")]
})
]
})
}
});
// define a lambda function to resize images
var imageResizeLambda = new Function(this, "ImageResizeLambda", new FunctionProps
{
Runtime = Runtime.DOTNET_8,
Handler = "ImageResizeLambda::ImageResizeLambda.Function::FunctionHandler",
Code = Code.FromAsset("../src/ImageResizeLambda/bin/Release/net8.0/linux-arm64/publish"),
Architecture = Architecture.ARM_64,
MemorySize = 512,
Timeout = Duration.Minutes(2),
Role = imageResizeLambdaRole,
Environment = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
["RESIZED_OBJECT_PATH"] = destinationFolder.ValueAsString
}
});
// add an event notification to the bucket to trigger the lambda function when an image is uploaded.
// prefix is used to filter the event notifications to only trigger when an image is uploaded to the source folder
s3Bucket.AddEventNotification(EventType.OBJECT_CREATED, new LambdaDestination(imageResizeLambda), new NotificationKeyFilter
{
Prefix = sourceFolder.ValueAsString + "/"
});
// allow the API lambda function to write objects to the bucket
var imageUploadApiLambdaRole = new Role(this, "ImageUploadApiLambdaRole", new RoleProps
{
AssumedBy = new ServicePrincipal("lambda.amazonaws.com"),
ManagedPolicies =
[
ManagedPolicy.FromAwsManagedPolicyName("service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole")
],
InlinePolicies = new Dictionary<string, PolicyDocument>
{
["S3Policy"] = new PolicyDocument(new PolicyDocumentProps
{
Statements = [
new PolicyStatement(new PolicyStatementProps
{
Actions = ["s3:PutObject"],
Resources = [s3Bucket.ArnForObjects("*")]
})
]
})
}
});
// define a lambda function to upload images
var imageUploadApiLambda = new Function(this, "ImageUploadApiLambda", new FunctionProps
{
Runtime = Runtime.DOTNET_8,
Handler = "ImageUploadApi",
Code = Code.FromAsset("../src/ImageUploadApi/bin/Release/net8.0/linux-arm64/publish"),
Architecture = Architecture.ARM_64,
MemorySize = 512,
Timeout = Duration.Minutes(2),
Role = imageUploadApiLambdaRole,
Environment = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
["BUCKET_NAME"] = bucketName.ValueAsString,
["UPLOAD_PATH"] = sourceFolder.ValueAsString
}
});
// define an API Gateway (HTTP) to upload images
_ = new HttpApi(this, "ImageUploadApi", new HttpApiProps
{
DefaultIntegration = new HttpLambdaIntegration(
"ImageUploadApiIntegration",
imageUploadApiLambda,
new HttpLambdaIntegrationProps
{
PayloadFormatVersion = PayloadFormatVersion.VERSION_2_0
}),
ApiName = "ImageUploadApi",
CorsPreflight = new CorsPreflightOptions
{
AllowOrigins = new[] { "*" },
AllowMethods = new[] { CorsHttpMethod.ANY },
AllowHeaders = new[] { "*" }
},
});
}
}
}How to deploy
You can deploy this solution using the following commands:
cd src
dotnet publish -c Release -r linux-arm64
cd ../cdk/src
cdk deploy --parameters BucketName=MyUniqueBucketName --parameters SourceFolder=images --parameters DestinationFolder=resized